
Some Links
2 years ago
A random walk down the world of business economics

Slavery still exists in
 Barking and Dagenham, in east London. With the fastest-growing birth rate in greater London over the decade to 2010 (up 58%), it also faces the biggest increase in demand for school places. At primary-school level this is set to rise by 43% between the academic years 2010-11 and 2015-16 (see map). Link
Barking and Dagenham, in east London. With the fastest-growing birth rate in greater London over the decade to 2010 (up 58%), it also faces the biggest increase in demand for school places. At primary-school level this is set to rise by 43% between the academic years 2010-11 and 2015-16 (see map). Link
 Cuba is getting older. “The typical Cuban family consists of two grandparents, two parents and one child,” says Jorge Mario Sánchez of CEEC. Link
Cuba is getting older. “The typical Cuban family consists of two grandparents, two parents and one child,” says Jorge Mario Sánchez of CEEC. Link
 The interesting article in The Economist discusses the position of women in the post-revolutionary era in the Arab world, in particularly in Tunisia and Egypt. Nevertheless, the contribution and emancipation of women in Jasmin revolution has been instrumental in defending richly deserved civil liberties and grater human freedom. From now on, the main challenge of newly-emerged Arab societies is not only to lay solid foundationa of democratic institutions and governance but, nevertheless, to promote the political and economic empowermant of women since the transition to a vibrant civil sociaty can not be accomplished, by any means, without extending the virtues of human freedom to women. Recent political development in post-revolutionary Egypt suggests the opposite since women have been excluded from the commission on the drafting of the new constitution. Moreover, recent polls have shown that 60 percent of Egyptians believe that Sharia law sould be the ultimate legal system in the country. If that is the case, it would certainly jeopardize the prospects of bringing civil liberties to the very infancy of world's (hopfully) prospective democracies. What women of Jasmin revolution fear is the (yet) unlikely possibility that civil liberties would vanish. Nevertheless, the experience from Iraq suggests that even though women suffered badly during Saddam's rule it should not be forgotten that mostly prior to 1991 women were free to work, go to school and walk the streets unveiled. Moreover, in the early years of Baath rule women were declared equal under law and were required to attend literacy classes. Hopefully, the Arab spring shall correct the failures of the past while acknowledging its rather rare but vital virtues.
The interesting article in The Economist discusses the position of women in the post-revolutionary era in the Arab world, in particularly in Tunisia and Egypt. Nevertheless, the contribution and emancipation of women in Jasmin revolution has been instrumental in defending richly deserved civil liberties and grater human freedom. From now on, the main challenge of newly-emerged Arab societies is not only to lay solid foundationa of democratic institutions and governance but, nevertheless, to promote the political and economic empowermant of women since the transition to a vibrant civil sociaty can not be accomplished, by any means, without extending the virtues of human freedom to women. Recent political development in post-revolutionary Egypt suggests the opposite since women have been excluded from the commission on the drafting of the new constitution. Moreover, recent polls have shown that 60 percent of Egyptians believe that Sharia law sould be the ultimate legal system in the country. If that is the case, it would certainly jeopardize the prospects of bringing civil liberties to the very infancy of world's (hopfully) prospective democracies. What women of Jasmin revolution fear is the (yet) unlikely possibility that civil liberties would vanish. Nevertheless, the experience from Iraq suggests that even though women suffered badly during Saddam's rule it should not be forgotten that mostly prior to 1991 women were free to work, go to school and walk the streets unveiled. Moreover, in the early years of Baath rule women were declared equal under law and were required to attend literacy classes. Hopefully, the Arab spring shall correct the failures of the past while acknowledging its rather rare but vital virtues.
 After having gained independence from colonial powers in 1950s, Arab countries adopted socialist model of economic development enhanced by heavy government intervention and political nationalism. The adoption of socialist public policies led to economic stagnation, institutionalized authocracy, often marred by millitary violence and civil war as in Algeria in early 1990s. The political and economic model of the typical Arab state is known for very low level of economic freedom even though structural indicators of Arab societies might indicate the opposite. Libya has steadily enjoyed the highest per capita income in North Africa. The country is the 15th largest oil exporter and has 9th largest prooved oil reserves in the World. However, Libya suffers heavily from 30 percent unemployment rate and diminished health and education outcomes. Libya's high GDP per capita is entirely inflated by high oil prices via excessive appreciation of the domestic exchange rate. Thus, as a developing country, Libya posts trade deficit while the country is a net exporter of capital flows. Excessive appreciation of Libyan currency, following high oil prices, is a potential source of Dutch disease - a triangle of slow productivity, weak domestic manufacturing sector and artificial wealth, created by a sudden surge of prices of natural resources without sufficient productivity growth. Therefore, Arab countries, from Qatar to Morocco, will have to undergo a swift transition to a competitive market economies, based on domestic structural change, rather than on artificial wealth increases, resulted from natural resource abundance.
After having gained independence from colonial powers in 1950s, Arab countries adopted socialist model of economic development enhanced by heavy government intervention and political nationalism. The adoption of socialist public policies led to economic stagnation, institutionalized authocracy, often marred by millitary violence and civil war as in Algeria in early 1990s. The political and economic model of the typical Arab state is known for very low level of economic freedom even though structural indicators of Arab societies might indicate the opposite. Libya has steadily enjoyed the highest per capita income in North Africa. The country is the 15th largest oil exporter and has 9th largest prooved oil reserves in the World. However, Libya suffers heavily from 30 percent unemployment rate and diminished health and education outcomes. Libya's high GDP per capita is entirely inflated by high oil prices via excessive appreciation of the domestic exchange rate. Thus, as a developing country, Libya posts trade deficit while the country is a net exporter of capital flows. Excessive appreciation of Libyan currency, following high oil prices, is a potential source of Dutch disease - a triangle of slow productivity, weak domestic manufacturing sector and artificial wealth, created by a sudden surge of prices of natural resources without sufficient productivity growth. Therefore, Arab countries, from Qatar to Morocco, will have to undergo a swift transition to a competitive market economies, based on domestic structural change, rather than on artificial wealth increases, resulted from natural resource abundance. The persistence of low fertility rate is one of the many factors inhibiting the stability of public pension systems in developed world. From the 20th century onwards fertility rates have plummeted in all countries that belong to high-income group. The causes of this systematic drop in average fertility rates could be attributed to income affects of higher education and human capital as well es to greater perticipation of women in the labor market. The fertility rate used to stand above average in countries where the dominance of hierarchical religion has been present. Catholic countries such as Ireland, Portugal and Spain were known for extensive influence of religion on fertility decisions regarding the number of children. Thanks to greater use of contraceptive means, the fertility rates in those countries have stadely converged to the level of fertility in Protestant countries. In recent years, the fertility rate in Catholic countries has been ranked at the bottom in high-income country group.
The persistence of low fertility rate is one of the many factors inhibiting the stability of public pension systems in developed world. From the 20th century onwards fertility rates have plummeted in all countries that belong to high-income group. The causes of this systematic drop in average fertility rates could be attributed to income affects of higher education and human capital as well es to greater perticipation of women in the labor market. The fertility rate used to stand above average in countries where the dominance of hierarchical religion has been present. Catholic countries such as Ireland, Portugal and Spain were known for extensive influence of religion on fertility decisions regarding the number of children. Thanks to greater use of contraceptive means, the fertility rates in those countries have stadely converged to the level of fertility in Protestant countries. In recent years, the fertility rate in Catholic countries has been ranked at the bottom in high-income country group.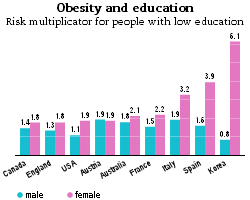 A very interesting estimate by the OECD shows that women with low level of education are far more likely than men to become obese.
A very interesting estimate by the OECD shows that women with low level of education are far more likely than men to become obese. Second, Cuban communist leaders looked up to the Soviet Union as a role model of the socialist society. By the time of the revolution, Cuba followed the course of destructive economic policy. It began imposing price controls and the trade with the rest of the world, except for the socialist countries, was ended. In addition, civil and personal liberties vanished under the communist regime. Therefore, Cuban economic model resulted in food shortages, land depletion, massive immigration and frequent oil crises.
Second, Cuban communist leaders looked up to the Soviet Union as a role model of the socialist society. By the time of the revolution, Cuba followed the course of destructive economic policy. It began imposing price controls and the trade with the rest of the world, except for the socialist countries, was ended. In addition, civil and personal liberties vanished under the communist regime. Therefore, Cuban economic model resulted in food shortages, land depletion, massive immigration and frequent oil crises. According to WSJ (link), Spain has finally implemented the broader reform of the labor market structure. Spain's 20 percent unemployment rate is the highest in the Euroarea. Traditionally, Spain was known for its notorious and heavily regulated labor market. The country used to maintain high levels of minimum wage and high cost of dismissal. The reform introduced by the Zapatero government removed the restrictions for dismissals on a fair basis and deregulated dismissal procedures on indefinite labor contracts. Dismissal cost has been decreased from 45 days to 33 days of salary per year worked.
According to WSJ (link), Spain has finally implemented the broader reform of the labor market structure. Spain's 20 percent unemployment rate is the highest in the Euroarea. Traditionally, Spain was known for its notorious and heavily regulated labor market. The country used to maintain high levels of minimum wage and high cost of dismissal. The reform introduced by the Zapatero government removed the restrictions for dismissals on a fair basis and deregulated dismissal procedures on indefinite labor contracts. Dismissal cost has been decreased from 45 days to 33 days of salary per year worked. Between 2001 and 2003, Bush administration enacted a series of tax cuts aimed at boosting the recovery of the U.S. economy from the 2001 recesion. In this year, tax rate on income in the lowest bracket was reduced to 10 percent while top marginal tax rate was slashed to 35 percent from 39.6 percent. Tax rates were also reduced for middle-income earners. In 2002, the administration reduced tax burden on new business investment while in 2003 tax rates on dividends and capital gains was decreased. These measures were a part of broader $1.35 trillion tax cut program approved by the Congress over a ten year course.
Between 2001 and 2003, Bush administration enacted a series of tax cuts aimed at boosting the recovery of the U.S. economy from the 2001 recesion. In this year, tax rate on income in the lowest bracket was reduced to 10 percent while top marginal tax rate was slashed to 35 percent from 39.6 percent. Tax rates were also reduced for middle-income earners. In 2002, the administration reduced tax burden on new business investment while in 2003 tax rates on dividends and capital gains was decreased. These measures were a part of broader $1.35 trillion tax cut program approved by the Congress over a ten year course. Countries such as Iran, Libya and Venezuela are among the largest oil-producing developing countries. In spite of vast supply of commodities, the data and experience do not suggest a positive impact of resources on economic growth. Prior to the 1979 Islamic revolution, Iran used to be one of the most developed countries in the Middle East. After 1979, Iran underwent an overhaul of its economic system and a beginning of large-scale state intervention in the economy. The theocratic government regime de facto suppressed private property rights and imposed strict government control over the economy. Even though Iran's oil reserves have been among the largest in the world, country's GDP per capita and structural indicators have stagnated since 1979.
Countries such as Iran, Libya and Venezuela are among the largest oil-producing developing countries. In spite of vast supply of commodities, the data and experience do not suggest a positive impact of resources on economic growth. Prior to the 1979 Islamic revolution, Iran used to be one of the most developed countries in the Middle East. After 1979, Iran underwent an overhaul of its economic system and a beginning of large-scale state intervention in the economy. The theocratic government regime de facto suppressed private property rights and imposed strict government control over the economy. Even though Iran's oil reserves have been among the largest in the world, country's GDP per capita and structural indicators have stagnated since 1979. The migration to developed countries has resulted in higher employment and greater specialization in the labor market. Without the flow of migrants the structure of the labor market in developed countries would incentivize workers to take lower paid jobs which would result in lower incomes. As the developed countries opened their borders to immigrants from all over the world, young individuals were enabled to invest in human capital and by doing so increase their career prospects. As for developing countries, migrants increase the stock of human capital availible to the country of migrant's origin. Therefore, immigration from less developed countries should not be seen as a loss but as an immense opportunity to get the know-how and high skills through which the country of migrant's origin shall prosper. The widespread emergence of technologies such as Google's applications, Twitter, Facebook, Linkedin etc. has further enhanced the flow of knowledge and information to the countries of migrant's origin. It should not be neglected that economic catch-up, generated from technological imitation, is the only way for less developed countries to reach the income per capita of their richer peers.
The migration to developed countries has resulted in higher employment and greater specialization in the labor market. Without the flow of migrants the structure of the labor market in developed countries would incentivize workers to take lower paid jobs which would result in lower incomes. As the developed countries opened their borders to immigrants from all over the world, young individuals were enabled to invest in human capital and by doing so increase their career prospects. As for developing countries, migrants increase the stock of human capital availible to the country of migrant's origin. Therefore, immigration from less developed countries should not be seen as a loss but as an immense opportunity to get the know-how and high skills through which the country of migrant's origin shall prosper. The widespread emergence of technologies such as Google's applications, Twitter, Facebook, Linkedin etc. has further enhanced the flow of knowledge and information to the countries of migrant's origin. It should not be neglected that economic catch-up, generated from technological imitation, is the only way for less developed countries to reach the income per capita of their richer peers. In the U.S., average Body Mass Index (BMI) for men is 26, one point above the critical level. Given widespread growth of childhood obesity, policymakers in Washington have pondered the idea of levying a tax on soda drinks and fast food. The consumption of these products has negative impact on bystanders. Moreover, due to obesity, insurance premiums and costs of health care are rising. Each year, childhood obesity raises insurance premiums by $147 billion. In addition, childhood obesity is likely to become the major source of future growth of Medicare costs. Although the obesity pattern is the strongest and most significant in the U.S., Europe is not immune to widespread childhood obesity. The highest percentage of overweight children in Europe was found in Spain, Greece, Germany and in the UK. In general, obesity rates in Europe are catching up the U.S. level.
In the U.S., average Body Mass Index (BMI) for men is 26, one point above the critical level. Given widespread growth of childhood obesity, policymakers in Washington have pondered the idea of levying a tax on soda drinks and fast food. The consumption of these products has negative impact on bystanders. Moreover, due to obesity, insurance premiums and costs of health care are rising. Each year, childhood obesity raises insurance premiums by $147 billion. In addition, childhood obesity is likely to become the major source of future growth of Medicare costs. Although the obesity pattern is the strongest and most significant in the U.S., Europe is not immune to widespread childhood obesity. The highest percentage of overweight children in Europe was found in Spain, Greece, Germany and in the UK. In general, obesity rates in Europe are catching up the U.S. level. Evidence suggests that living in one-parent household increases the probability of child poverty. In the OECD, 85 percent of single-parent households are headed by women. The highest percentage of single-parent households prevails in English-speaking countries (US, UK, Canada and New Zealand). The highest proportion of children aged 14 or below and living in one-parent household was found in the US (25.8 percent), Estonia (24 percent), the UK (22.9 percent). The lowest proportion was found in Portugal (9.8 percent), Italy (9.2 percent) and Greece (7.4 percent). It seems that the proportion is closely related to the religious pattern of the society, meaning that more traditional societies emphasize long term marriage and matrimony stability. The issue deserves more attention as the childrens' wellbeing, earnings and state of health are, in a large part, determined in early childhood.
Evidence suggests that living in one-parent household increases the probability of child poverty. In the OECD, 85 percent of single-parent households are headed by women. The highest percentage of single-parent households prevails in English-speaking countries (US, UK, Canada and New Zealand). The highest proportion of children aged 14 or below and living in one-parent household was found in the US (25.8 percent), Estonia (24 percent), the UK (22.9 percent). The lowest proportion was found in Portugal (9.8 percent), Italy (9.2 percent) and Greece (7.4 percent). It seems that the proportion is closely related to the religious pattern of the society, meaning that more traditional societies emphasize long term marriage and matrimony stability. The issue deserves more attention as the childrens' wellbeing, earnings and state of health are, in a large part, determined in early childhood. Cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) are the main cause of deaths in the Europe, approximately 49 percent of all deaths, out of which 30 percent of all premature deaths before the age of 65. Cardiovascular diseases are estimated to cost the EU €169 billion every year.
Cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) are the main cause of deaths in the Europe, approximately 49 percent of all deaths, out of which 30 percent of all premature deaths before the age of 65. Cardiovascular diseases are estimated to cost the EU €169 billion every year. The lawmakers in Florida have considered cutting the 6 percent boat registration tax. Florida already has one of the highest sales taxes in the US. Buying a $1 million boat will cost you $60.000 in sales tax. In nearby states such as North Carolina, yacht registration costs you $1.500 at most, whereas only $600 in Rhode Island and $500 in South Carolina. Even more attractive are Cayman Islands where you pay close to zero tax on yacht registration. Because of Florida's uncompatitive tax regime, 8 out of 10 boats in the state are registraed somewhere else, either in other costal states or abroad. The message is clear, raising taxes is tempting but in reality it leads either to tax evasion or capital escape. Higher tax rate lead to the opposite results of what the policymakers expected. Their decision costs Florida $120 million in lost revenue.
The lawmakers in Florida have considered cutting the 6 percent boat registration tax. Florida already has one of the highest sales taxes in the US. Buying a $1 million boat will cost you $60.000 in sales tax. In nearby states such as North Carolina, yacht registration costs you $1.500 at most, whereas only $600 in Rhode Island and $500 in South Carolina. Even more attractive are Cayman Islands where you pay close to zero tax on yacht registration. Because of Florida's uncompatitive tax regime, 8 out of 10 boats in the state are registraed somewhere else, either in other costal states or abroad. The message is clear, raising taxes is tempting but in reality it leads either to tax evasion or capital escape. Higher tax rate lead to the opposite results of what the policymakers expected. Their decision costs Florida $120 million in lost revenue. Source: World Bank
Source: World Bank Source: Eurostat
Source: Eurostat
 Soccer Power Index is a statistical measure of team power in world soccer. It is an interesting tool to predict soccer match results. Countries are ranked on the basis of Fifa points and past performance. The scale contains 211 national teams.
Soccer Power Index is a statistical measure of team power in world soccer. It is an interesting tool to predict soccer match results. Countries are ranked on the basis of Fifa points and past performance. The scale contains 211 national teams.
 Source: FiveThirtyEight
Source: FiveThirtyEight
 Source: China Statistical Yearbook (2005)
Source: China Statistical Yearbook (2005)
 Source: European Commission (2009)
Source: European Commission (2009)